Common Problems
Priniting the combination of an array of particular size.
class Solution { public static void findCombinations(int[] A, int i, int k, List<Integer> out) { if (k == 0) { //Operation with List<Integer> out return; } // start from the next index till the last index for (int j = i; j < A.length; j++) { out.add(A[j]); findCombinations(A, j + 1, k - 1, out); out.remove(out.size() - 1); // backtrack } }}class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) { List<List<Integer>> output = new ArrayList(); output.add(new ArrayList<Integer>()); for (int num : nums) { List<List<Integer>> newSubsets = new ArrayList(); for (List<Integer> curr : output) { newSubsets.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(curr){{add(num);}}); } for (List<Integer> curr : newSubsets) { output.add(curr); } } return output; }}class Solution { public static void main(String[] args){ int[] A = { 1, 2, 3 }; int k = 2; System.out.println(findCombinations(A, 0, k, new ArrayList<>())); // If you want to print out all the combination then you can put a for loop // on the length of the A starting from 1. }}// This is a call to the left method for printing out the combination of length 2 from the array.Printing all the possible paths of a binary tree.
class Solution { public void printAllPathsBinaryTree(TreeNode root) { ArrayList<Integer> path = new ArrayList<Integer>(); printPathsBinaryTree(root, path); } public void printPathsBinaryTree(TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> path) { if (root == null) { return; } path.add(root.data); if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { System.out.println(path); } printPathsBinaryTree(root.left, path); printPathsBinaryTree(root.right, path); path.remove(path.size() - 1); }}APPLICATIONS
- Can be used to calculate the longest path from any node to targeted node.
- Can be used to find the path with all the equal values in them.
Permutation of an array.
class Solution { void permutate(int[] array, int start) { if (start == array.length) { //computations. return; } for (int i = start; i < array.length; ++i) { this.swap(array, i, start); this.permutate(array, start + 1); this.swap(array, i, start); } } void swap(int[] array, int i, int j) { if (i != j) { int temp = array[i]; array[i] = array[j]; array[j] = temp; } }}Roman to Integer.
class Solution { public int romanToInt(String S) { int ans = 0, num = 0; for (int i = S.length()-1; i >= 0; i--) { switch(S.charAt(i)) { case 'I': num = 1; break; case 'V': num = 5; break; case 'X': num = 10; break; case 'L': num = 50; break; case 'C': num = 100; break; case 'D': num = 500; break; case 'M': num = 1000; break; } if (4 * num < ans) ans -= num; else ans += num; } return ans; }}class Solution:
def romanToInt(self, s: str) -> int:
translations = {
"I": 1,
"V": 5,
"X": 10,
"L": 50,
"C": 100,
"D": 500,
"M": 1000
}
number = 0
s = s.replace("IV", "IIII").replace("IX", "VIIII")
s = s.replace("XL", "XXXX").replace("XC", "LXXXX")
s = s.replace("CD", "CCCC").replace("CM", "DCCCC")
for char in s:
number += translations[char]
return number
Rotate a Matrix.
class Solution { public void rotate(int[][] matrix) { transpose(matrix); reflect(matrix); } public void transpose(int[][] matrix) { int n = matrix.length; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) { int tmp = matrix[j][i]; matrix[j][i] = matrix[i][j]; matrix[i][j] = tmp; } } } public void reflect(int[][] matrix) { int n = matrix.length; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n / 2; j++) { int tmp = matrix[i][j]; matrix[i][j] = matrix[i][n - j - 1]; matrix[i][n - j - 1] = tmp; } } }}Spiral Matrix.
class Solution { public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) { List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList(); if(matrix == null||matrix.length == 0){ return nums; } int size = matrix[0].length * matrix.length; int top = 0; int bottom = matrix.length-1; int left = 0; int right = matrix[0].length-1; while(nums.size()<size){ for(int i=left; i<=right && nums.size()<size;i++){ nums.add(matrix[top][i]); } top++; for(int i=top; i<=bottom && nums.size()<size;i++){ nums.add(matrix[i][right]); } right--; for(int i=right;i>=left && nums.size()<size;i--){ nums.add(matrix[bottom][i]); } bottom--; for(int i=bottom;i>=top && nums.size()<size;i--){ nums.add(matrix[i][left]); } left++; } return nums; }}House Robber.
class Solution { public int rob(int[] nums) { if(nums.length == 1) return nums[0]; int[] dp = new int[nums.length]; dp[0] = nums[0]; dp[1] = nums[1]; dp[1] = Math.max(nums[0],nums[1]); for(int i = 2;i<nums.length;i++){ dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i-1],dp[i-2]+nums[i]); } return dp[dp.length-1]; }}Number of Islands.
class Solution { public int numIslands(char[][] grid) { int result = 0; if(grid == null || grid.length == 0) return 0; for(int i=0;i<grid.length;i++){ for(int j=0;j<grid[i].length;j++){ if(grid[i][j] == '1'){ result += dfs(grid, i, j); } } } return result; } public int dfs(char[][] grid, int i, int j){ if(i<0 || i>=grid.length || j<0 || j>=grid[i].length || grid[i][j] == '0'){ return 0; } grid[i][j] = '0'; dfs(grid,i+1,j); dfs(grid,i-1,j); dfs(grid,i,j+1); dfs(grid,i,j-1); return 1; }}Count Primes
public class Solution { public int countPrimes(int n) { boolean[] notPrime = new boolean[n]; int count = 0; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) { if (notPrime[i] == false) { count++; for (int j = 2; i*j < n; j++) { notPrime[i*j] = true; } } } return count; }}Maximal Square.
dp(i,j)= (min(dp(i−1,j),dp(i−1,j−1),dp(i,j−1))) +1.
public class Solution { public int maximalSquare(char[][] matrix) { int rows = matrix.length, cols = rows > 0 ? matrix[0].length : 0; int[][] dp = new int[rows + 1][cols + 1]; int maxsqlen = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= rows; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= cols; j++) { if (matrix[i-1][j-1] == '1'){ dp[i][j] = (Math.min(Math.min(dp[i][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j]),dp[i - 1][j - 1])) + 1; maxsqlen = Math.max(maxsqlen, dp[i][j]); } } } return maxsqlen * maxsqlen; }}Trapping Rain Water
Problem Statement
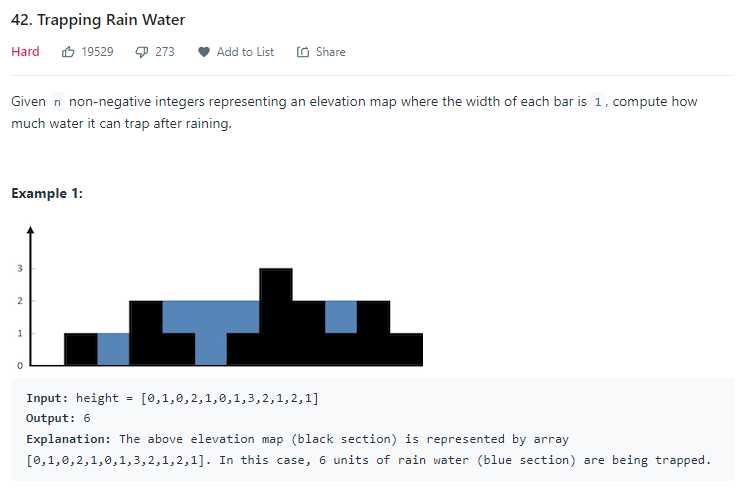
Calculate maxLeft and maxRight for each row.
Then, for each row, find the Math.min of the two for every index and subtract it from the current index height.
Math.min(maxLeft[i], maxRight[i]) - height[i] is the maximum water that can be trapped in the ith row.
Solution
- Method 1 - Extra Space
- Method 2 - No Space
public int trap(int[] height) {
int n = height.length;
if (n <= 2) return 0;
// pre-compute
int[] leftMax = new int[n];
int[] rightMax = new int[n];
leftMax[0] = height[0]; // init
rightMax[n - 1] = height[n - 1];
for (int i = 1, j = n - 2; i < n; ++i, --j) {
leftMax[i] = Math.max(leftMax[i - 1], height[i]);
rightMax[j] = Math.max(rightMax[j + 1], height[j]);
}
// water
int totalWater = 0;
for (int k = 1; k < n - 1; ++k) { // do not consider the first and the last places
int water = Math.min(leftMax[k - 1], rightMax[k + 1]) - height[k];
totalWater += (water > 0) ? water : 0;
}
return totalWater;
}
// TC : O(n)
// SC : O(n)
public int trap(int[] height) {
if (height.length==0) return 0;
int left = 0, right = height.length-1;
int leftMax=0, rightMax=0;
int ans = 0;
while (left < right) {
if (height[left] > leftMax) leftMax = height[left];
if (height[right] > rightMax) rightMax = height[right];
if (leftMax < rightMax) {
ans += Math.max(0, leftMax-height[left]);
left++;
} else {
ans += Math.max(0, rightMax-height[right]);
right--;
}
}
return ans;
}
// TC : O(n)
// SC : O(1)
Next Permutation
Problem Statement
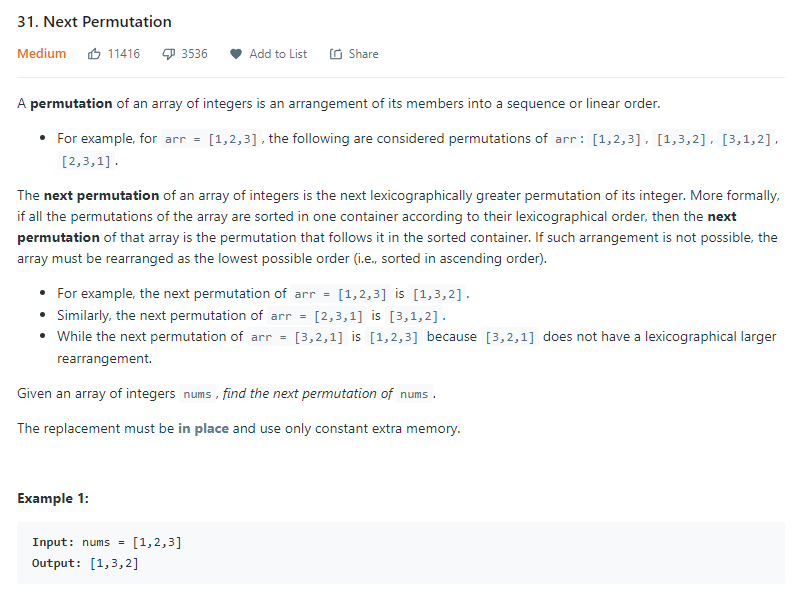
Consists of Two Parts one is finding the highest and just lowest element to the highest when starting from the end.
Then we can swap the highest and lowest element and reverse the rest of the elements, to the index that was found.
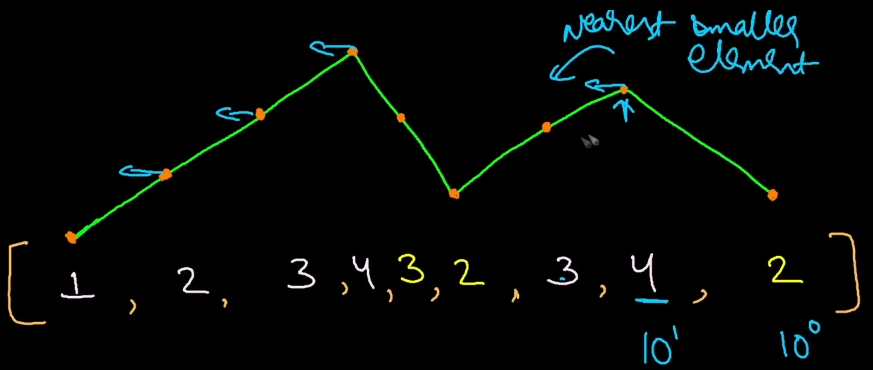
class Solution {
public void swap(int arr[], int i, int j){
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
public void reverse(int arr[], int i, int j){
while(i < j) swap(arr, i++, j--);
}
public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length <= 1) return;
int i = nums.length - 2;
while(i >= 0 && nums[i] >= nums[i+1]) i--;
if(i >= 0){
int j = nums.length - 1;
while(nums[j] <= nums[i]) j--;
swap(nums, i, j);
}
reverse(nums, i+1, nums.length - 1);
}
}
// TC : O(n)
// SC : O(1)
Largest Plus Sign
Problem Statement
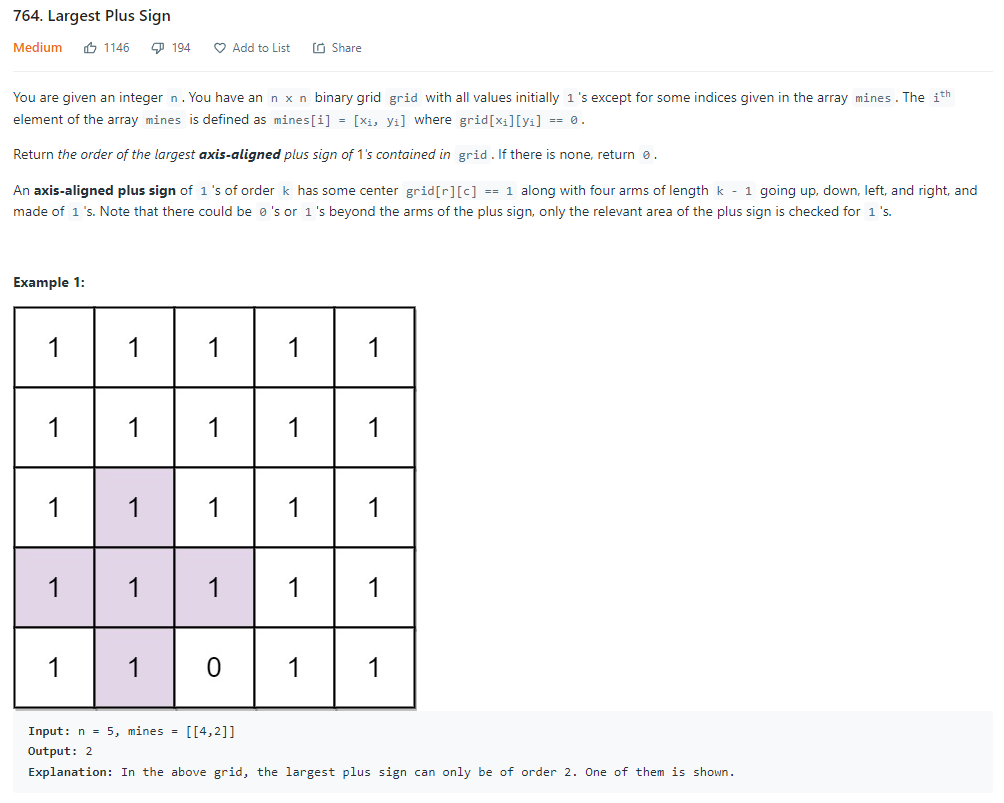
- Explanation
- Solution - DP
Using DP would be a good idea. There will be two process involved in the making of the 2D Dimensional Array. First, we will make a 2D Array of size (Rows, Columns) and fill it with 0. Second we would fill the 2D DP Array with the count or extension of how much 1's are present in the left and right of the array.
For example, if we have the following array given in the problem statement. We would have to create a first iteration Matrix like this:
Secondly we would have to apply our mind to producing the array matrix as below:
At the same time we would keep a ans counter which will be calculating the largest plus sign.
class Solution {
public int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, int[][] mines) {
Set<Integer> banned = new HashSet();
int[][] dp = new int[N][N];
for (int[] mine: mines)
banned.add(mine[0] * N + mine[1]);
int ans = 0, count;
for (int r = 0; r < N; ++r) {
count = 0;
for (int c = 0; c < N; ++c) {
count = banned.contains(r*N + c) ? 0 : count + 1;
dp[r][c] = count;
}
count = 0;
for (int c = N-1; c >= 0; --c) {
count = banned.contains(r*N + c) ? 0 : count + 1;
dp[r][c] = Math.min(dp[r][c], count);
}
}
for (int c = 0; c < N; ++c) {
count = 0;
for (int r = 0; r < N; ++r) {
count = banned.contains(r*N + c) ? 0 : count + 1;
dp[r][c] = Math.min(dp[r][c], count);
}
count = 0;
for (int r = N-1; r >= 0; --r) {
count = banned.contains(r*N + c) ? 0 : count + 1;
dp[r][c] = Math.min(dp[r][c], count);
ans = Math.max(ans, dp[r][c]);
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Re-organize String
- Problem Statement
- Approach/Solution
Idea behind the approach is that we have to sort the Characters in the String as per their frequencies.
And further we pop out the two Characters with the max frequency and the second max frequency and add to a new String.
Remember: Only the two Characters with the Max and Second Max frequencies will be alternating characters in output String. PriorityQueue will be used to maintain the frequencies of the Characters as per their sorted order.
class Solution {
public String reorganizeString(String s) {
// get the count of each count
Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (char ch: s.toCharArray())
map.put(ch, map.getOrDefault(ch, 0) + 1);
// use priority queue as maxHeap and use lambdas based on the count
PriorityQueue<Character> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> map.get(b) - map.get(a));
maxHeap.addAll(map.keySet());
// make the most frequent letter, then the next frequent letter and so on
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (maxHeap.size() > 1) {
char current = maxHeap.remove(); // maximum frequent
char next = maxHeap.remove(); // next max
sb.append(current);
sb.append(next); // alternatively adding
map.put(current, map.get(current) - 1);
map.put(next, map.get(next) - 1);
// if still the count > 0, add the charcaters back to heap
if (map.get(current) > 0)
maxHeap.add(current);
if (map.get(next) > 0)
maxHeap.add(next);
}
if (!maxHeap.isEmpty()) {
char last = maxHeap.remove();
if (map.get(last) > 1)
return "";
sb.append(last);
}
return sb.toString();
}
}